Department Of
Microbiology
TEACHING LEARNING METHODS
- Lecture classes
Lecture classes are taken where information on a particular topic is delivered via a speech (traditional board and chalk) or presentation (PowerPoint) by the faculty. Involves a large group of students (MBBS / Nursing / SAHS).
- Tutorials and small group discussions
Here a topic is explained for a particular period to an individual or very small group of students. Also includes question paper discussion, doubt clearance, etc. Each faculty is in-charge of 15 MBBS students.
- Seminars
Students are given the topics for a seminar in advance and they present the same after which it is discussed by the faculty in charge. Seminars in the applied and important (must-know areas) topics are taken for every batch after the completion of a major part of the syllabus.
- Symposium/CME
Every year the department conducts symposia/CME on various topics such as “Dengue, TB Day, Hepatitis Day, Rabies Day and World AIDS Day” and invites guest lecturers from other institutions as well as internal speakers from other departments and within the department.
- Self-study
After completion of the syllabus, students are allowed to do self-study and get their doubts cleared by the faculty in charge. This way it allows the student to pay attention to gain knowledge of an academic subject without assistance from a teacher.
- Practical classes and demonstrations
During practical hours, the faculty in charge gives a brief introduction about the practical class (aim, procedure, observation, inference) and then demonstrates the procedure and outcome after which students have to perform. This helps in the application of the knowledge and better understanding of the subject.
- Problem-based learning
A case scenario is discussed with students along with questions related to it. This process allows the learners to develop skills which they need for their future practice.
- Simulations / Models / Charts
Simulations are used in practical classes which reduce the risk of infection and also demonstrate the biochemical reactions for various microorganisms. Models of viruses and various culture media are present in the department Museum which help students understand the 3D structures. Charts help in identifying rare organisms and their phenotypic characteristics.
- Video clips
- Video clippings are used: To teach the pathogenesis of microorganisms
- For sample collection procedures
- To demonstrate certain procedures of rapid kit tests, etc. in-lab diagnosis
- For applied topics like Biomedical waste management
- Virology – Life cycle and pathogenesis
- Parasitology – Life cycles and pathogenesis
- Mycology procedures
- Journal clubs, Culture seminars, Topic seminars – PG students
One faculty as coordinator is assigned for every programme. Discussions on the latest journals help update knowledge.
Culture seminar gives practice for students to explore cultural characteristics and biochemical reactions and identify the given isolate (pure/mixed cultures).
Important topics are given to prepare and present at topic seminars as a way to gain broad knowledge about the subject.
- Integrated teaching
Integrated teaching is practised with other departments which create a bridge between academic knowledge and practical application. Topics such as HIV, diarrheal diseases, hepatitis, tuberculosis, malaria, and sexually transmitted diseases are taken.
- Microteaching
Microteaching is practised especially before practical classes to maintain uniformity.
- Clinical postings
Students have clinical postings in a batch of 5 for 7 days. This helps students gain a better understanding and develop an interest in the subject.
- Zoom online classes
In this critical moment of the global pandemic with COVID-19, we have started Zoom online classes for students where we can discuss topics and clear their doubts, post videos, etc. for continued teaching and learning.
- Workshops
Planned for workshops in future on
- Antimicrobial stewardship
- Hospital infection
- Emerging and re-emerging infections
| S.No. | Facility | Features |
| 1 | Bacteriology Lab |
|
| 2 | Molecular Diagnostic Lab |
|
| 3 | Mycobacteriology Lab |
|
| 4 | Research lab |
|
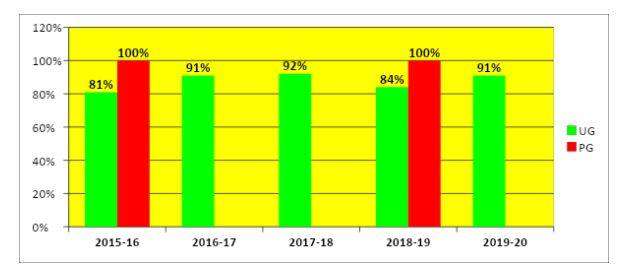
STUDENT OUTCOME:
PATIENT CARE:
Our department plays an important role in the diagnosis of infectious diseases, starting from the regular surveillance, treatment, control and prevention of any infectious disease. A microbiologist is an active member of the hospital infection control committee (HICC) and the antimicrobial stewardship group, thereby preventing many healthcare-associated infections/ post-operative wound infections from occurring at hospitals. We provide 24/7 laboratory services being a major part of the central laboratory and one faculty is posted for holiday duties in the department. Emergency direct collection of specimens from wards on request is also being provided for needy patients. We have a NABL accredited RT-PCR lab for the detection of COVID-19 in and around Pondicherry.
Regular surveillance of operation theatres, blood banks, and critical care high-definition units/ICUs/NICUs are done as a part of prevention against infection.






